Recently, I have consulted friends in the industry about the problem of the welding nut tripping slip. The following is a description of the welding nut used for a reference. For your reference! Anyone who has any ideas can also leave a message to discuss.
In the case of space structure (such as closed structure, when the space is small, the nut fixing device cannot be placed), the welding nut is generally used, and the convex welding nut is often used. Sometimes, in order to ensure the welding strength, the arc welding nut is also used. The nut is welded to the structural member body and tightened by tightening the bolt.
The projection welding nut is generally divided into a hexagonal flange face projection welding nut, a square welding nut, a hexagonal welding nut, etc. When the welding nut is selected, a square welding nut and a hexagonal welding nut are generally preferred. If the support surface is too small and the contact stress does not meet the design requirements, use a hexagonal flange face weld nut. In order to prevent welding spatter and electrophoretic paint from adhering to the threads of the weld nut, the NYCOTE coating is generally applied to the thread of the weld nut.

The hexagonal flange face welding nut standard mainly includes QC/T872-2011 welded hex flange nut (Fig. 12), VW60455 hex flange face weld nut and GMW3236 hex flange face weld nut. All three hex flange face weld nuts are based on the ISO21670 standard, but the QC/T872 standard has a convex-point weld pattern with a right-angled triangular tip that differs from other standard isosceles triangles.

The performance grades of the standard hexagonal flange face weld nuts of QC/T872 and GMW3236 meet the requirements of class 10 nuts, while the hexagonal flange face weld nuts of VW60455 standard meet level 10 (no quenching and tempering treatment) and level 12 (for The requirements of quenching and tempering treatment need to be flexibly selected according to the design requirements when selecting the hexagonal flange surface welding nut.
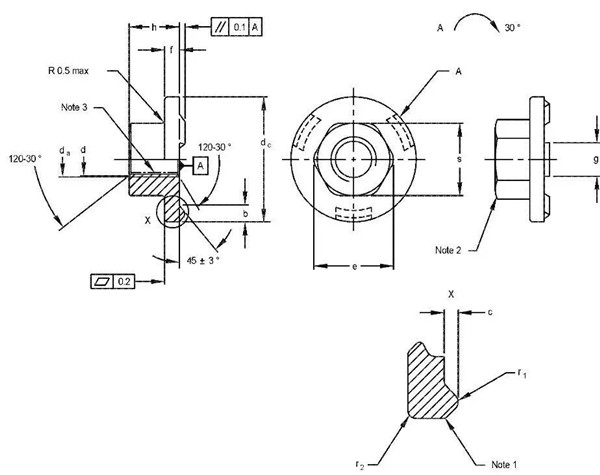   
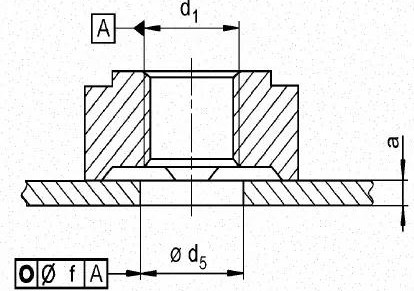
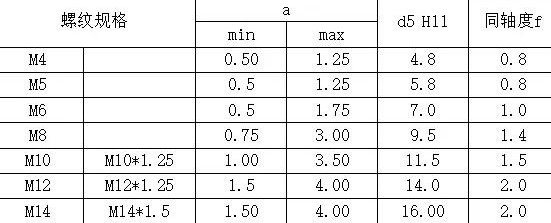
  The weld plate thickness of the hexagonal flange face weld nut and the hole size of the bolt hole are as follows.
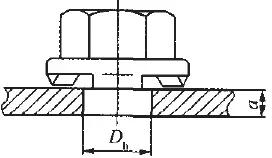
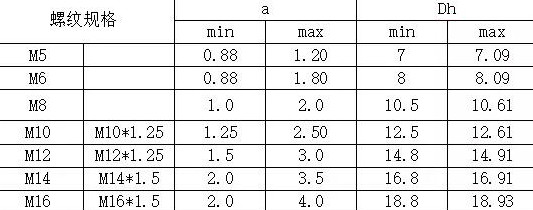
Hexagon flange face welded nut plate thickness and hole diameter requirements
Commonly used standards for square welding nuts are GB/T13680, VW60432, VW60449, in which GB/T13680 standard square welding nuts ensure the load is between 6 and 8 nuts to ensure the load, especially pay attention to between 6 and 8 levels. It is often guaranteed that the load meets the standard requirements, but when it is tightened with the 8.8 or even 10.9 bolts, the sliding of the sliding teeth will occur; at the same time, the GB/T13680 and VW60432 standard welding nut heights are exactly the same, and the VW60449 welding nut The height dimension is larger than the GB/T13680 and VW60432 height dimensions.
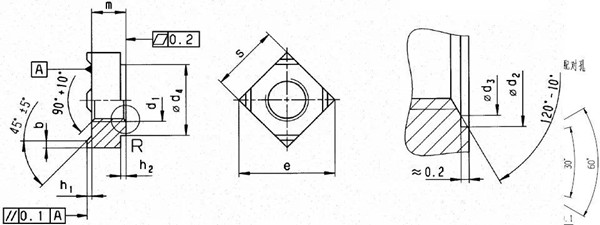   
  The welded plate thickness of the square welded nut and the hole size of the bolt hole are as follows.
Square weld nut thickness and hole diameter requirements
In addition to the above standard welded nuts, non-standard welded nuts can also be seen in Japanese models, only the internal threaded cylinder made of low carbon steel replaces the standard welded nut. The height of this welded nut It is also significantly higher than the standard height, in order to ensure a sufficient mesh length.
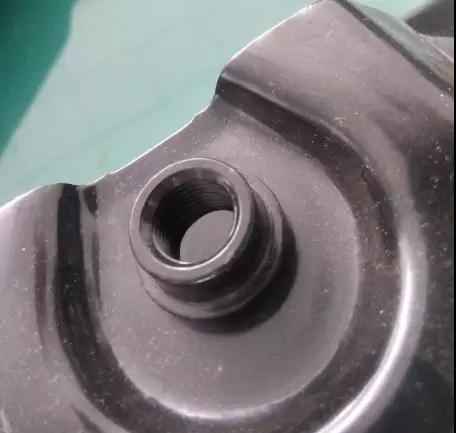

Figure Non-standard welding nut used in Japanese cars
The guaranteed load in the weld nut is tested before welding to meet the design requirements. After the weld nut is welded, it may cause the guaranteed load of the weld nut to decrease due to the heat of the weld. Therefore, the weld nut that matches the bolt can be selected with a weld nut one grade higher than the bolt.
Nuts with no tempering heat treatment coating and bolts with a strength class of ≤ 8.8 (according to DIN EN ISO 898-1), this ensures that even in the event of a bolt break, the nut does not Will cause damage.
The following explanation is given by means of superelastic tightening:
example 1:
Bolt M8, strength 10.9, when the torque angle method is used to yield and tighten, the pre-tightening force is 29000 N to 36000 N. In order to ensure that the thread of the nut does not slip when the superelastic over-yield is tightened, the estimated actual preload of the bolt and nut may be increased by another 10% (because the guaranteed load measured with the hardened mandrel is often measured by bolts) About 10% higher).
This expected installation preload is between 31900 N and 39600 N.
The weld nut of size M8 guarantees a load test force of 38100 N.
That is to say, in some cases, when the 10th grade nut and the 10.9 grade bolt are paired, when the superelastic over-yield is tightened, the weld nut of the 10-stage guaranteed load may have the possibility of the nut thread slippery.
Example 2:
Bolt M8, strength 8.8, when the yield is exceeded by the torque angle method, the pre-tightening force is seen as 19500 N to 26000 N. In order to ensure that the thread of the nut does not slip when the superelastic over-yield is tightened, the estimated actual pre-tension of the bolt and nut may be increased by another 10%.
The expected pre-tightening force is 21450 N to 28600 N. Under this preload, a 10-stage nut is used to ensure the load. The weld nut without heat treatment is not required to have the nut thread slip.
In addition, according to the calculation, the bolt with theoretical maximum yield strength, tensile strength and minimum friction number may also have an additional 20% installation preload. Therefore, the general welding nut is permanently welded to the structural member. In order to ensure that the thread of the welding nut does not cause sliding tooth damage, the design may require a welding nut matched with the 8.8-class bolt to ensure that the load satisfies the 10-level nut guaranteed load ( High specification, nut height is about 1×d, welding square nut and welded hex flange nut are not required for quenching and tempering. The welding nut matched with the 10.9 bolt ensures that the load meets the 12-level nut guaranteed load (high specification) The height of the nut is about 1×d, and it is required to weld the square nut and weld the hexagonal flange nut.
In summary, when designing the welding nut, in order to ensure that the thread sliding teeth are not tripped, at the same time, the welding nut generally needs to be subjected to electrophoresis after welding, which often causes the electrophoretic paint to be applied to the thread, which is equivalent to reducing The size of the thread is more difficult to screw in when it is tightened with the bolt. It is often seen in the workshop that tapping or wire processing is required. Therefore, it is recommended to use the glued anti-weld slag anti-electrophoresis for the welded nut or Design tolerances for larger clearances between bolt threads, such as 6E weld nut tolerances. Weld nut tolerances and threading problems are discussed in detail later in this microsignal. When designing the welding nut, it is recommended to design the strength of the welding nut to be higher than the original required nut, so that the sliding of the sliding tooth does not generally occur.
Fabe Stove Knob Lock could be used in most types of gas stove knobs. Exquisite and durable design, simple operation. Mulit-Colors would add the beauty of your house while the transparent stove lock would not influence the great looking of your furnitures. This is really useful housework helper that could effectively avoid your children open the gas stove knob by accident, in order to create a safety situation for your family.
Stove Knob Lock
Universal Stove Knob Lock,Urgent Stove Knob Lock,Reliable Stove Knob Lock,Stove Knob Lock
Ningbo Fabe Child Safety Co., Ltd. , https://www.fabesafe.com